What Is Fdm 3D Printing?
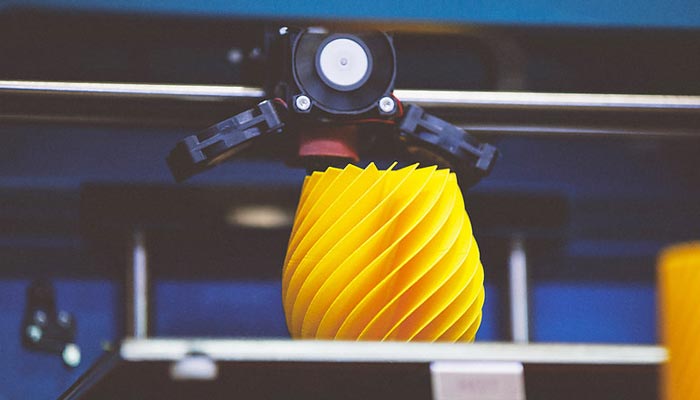
FDM 3D printing, or Fused Deposition Modeling, is a type of additive manufacturing technology. It works by depositing material in layers to build up an object. This is the most common type of 3D printing, and it is often used for prototyping and small-scale production.
FDM printers are available in a variety of sizes and price points, making them a good option for both personal and professional use.
FDM 3D printing is a popular type of 3D printing that uses filaments to create three-dimensional objects. The process works by melting the filament and then extruding it through a nozzle to create layers that build up to form the desired object. FDM 3D printers are often used for prototyping and manufacturing, as they offer a wide range of materials and colors to choose from.
What is Fused Deposition Modeling
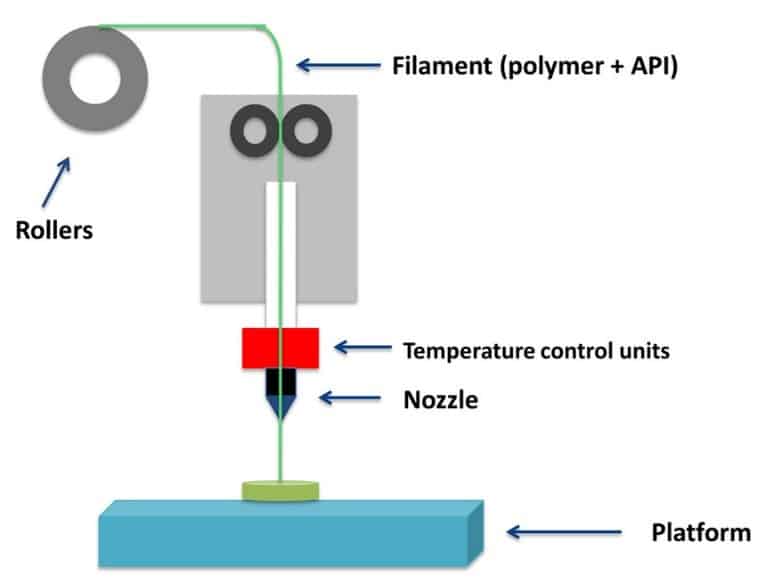
In fused deposition modeling (FDM), a solid object is created by successively depositing material in layers. The material is extruded from a nozzle, and the shape of the object is determined by the path of the nozzle as it moves across a build platform. FDM is an additive manufacturing technique, meaning that objects are built up layer by layer rather than being machined from a single piece of material.
FDM technology was invented in the 1980s by S. Scott Crump, who founded Stratasys Ltd., one of the leading manufacturers of FDM machines. FDM was originally developed for prototyping applications, but it has since been used to create functional parts and end-use products. FDM works with a variety of materials, including thermoplastic polymers, metals, ceramics, and composites.
So what materials does FDM use? You’ll require a thermoplastic of some sort, or a substance that can be molded when heated. This enables the adhesion of each layer as it is being created. With so many various thermoplastic varieties available, you may pick the one that works best for a particular design.
The FDM process begins with creating a digital 3D model of the object to be printed. This model can be created using computer-aided design (CAD) software or scanned from an existing physical object using 3D scanning technology.
stl file format which can be imported into slicing software. Slicing software “slices” the 3D model into thin layers which will be used by the FDM machine to build up the object layer by layer. The slicing software also generates G-code instructions which tell the FDM machine how to move the extrusion head and build platform to create each layer according to the digital model.
Is Fdm And Pla the Same?
No, FDM and PLA are not the same. FDM is short for Fused Deposition Modeling, which is a type of 3D printing technology. PLA, on the other hand, is short for Polylactic Acid, which is a type of thermoplastic material.
So while they are both related to 3D printing technology and materials, they are not the same thing.
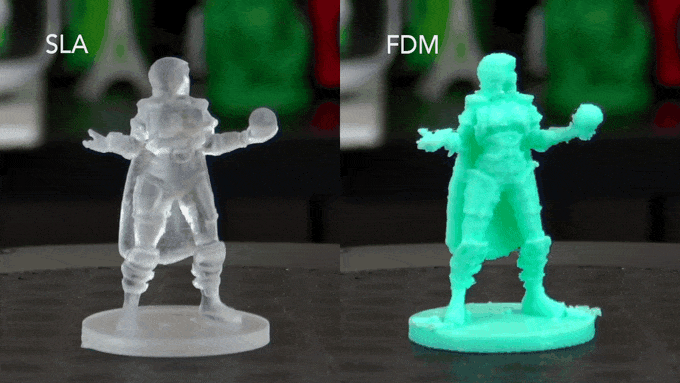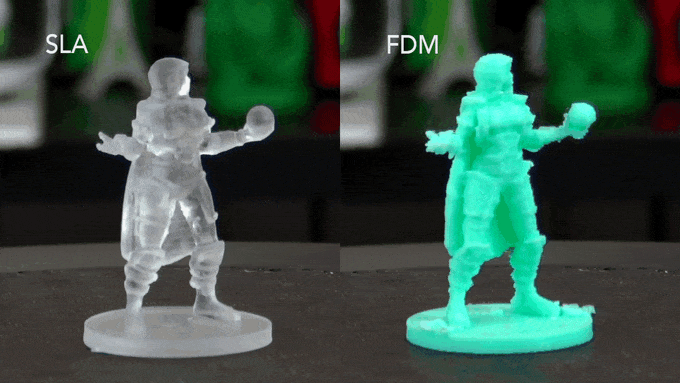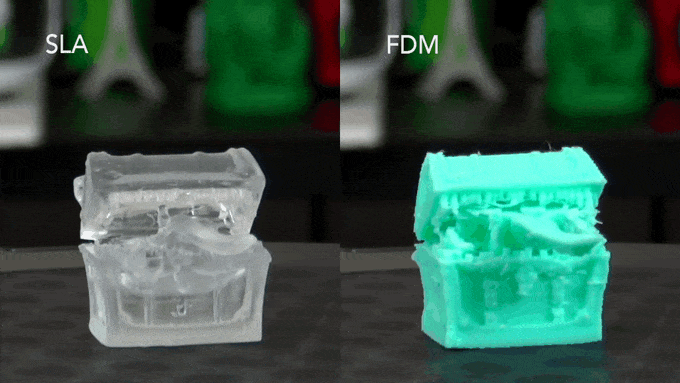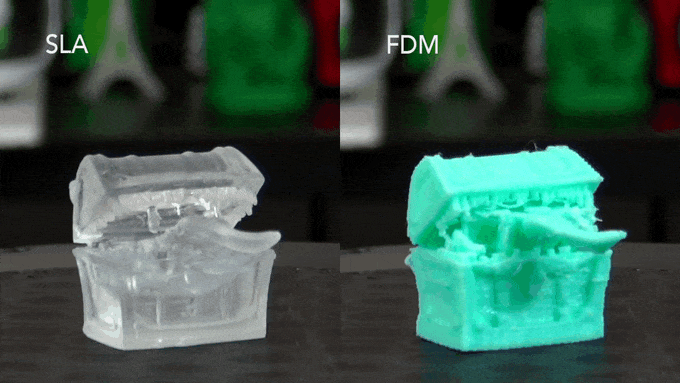
What is the Difference between Fdm And Sla?
FDM vs SLA 3D printing technology has come a long way since it was first invented in the 1980s. Today, there are many different types of 3D printers available on the market, each with its own unique set of features and capabilities.
Two of the most popular 3D printing technologies are FDM (fused deposition modeling) and SLA (stereolithography). So, what’s the difference between these two technologies? FDM is a type of 3D printing technology that works by extruding melted plastic filaments through a nozzle to build up layers of material.
This process is similar to how traditional 2D printers work, except in three dimensions. FDM printers are typically very affordable and easy to use, making them a popular choice for home and hobbyist users. However, FDM prints can have visible layer lines and are not as accurate or detailed as prints made with other technologies such as SLA.
SLA is a type of 3D printing technology that uses an ultraviolet laser to cure photosensitive resin into solid layers. This process produces prints that are much smoother and more detailed than those made with FDM technology. SLA printers are typically more expensive than FDM printers, but they offer superior print quality.
Which is Stronger Fdm Or Sla?
There are a few different ways to judge the strength of 3D printing technologies. One way is to look at the technology’s ability to produce strong and precise parts. In this respect, FDM technology is stronger than SLA.
This is because FDM uses filaments made of ABS, PLA, or other tough polymers. These materials are extruded layer by layer in order to build up an object. The result is a tough and precise 3D printed part.
SLA works differently than FDM. It uses a laser to cure resin into solid objects. The resin used in SLA printers is not as strong as the filaments used in FDM printers.
As a result, SLA-printed parts are not as strong or precise as FDM-printed parts. Another way to compare the strength of 3D printing technologies is to look at their ability to produce large objects quickly and efficiently. Here again, FDM has an advantage over SLA technology.
This is because FDM can print much larger objects than SLA can handle efficiently. For example, an average sized object that could be printed on an FDM printer might take several hours whereas the same-sized object printed on an SLA printer would take days or weeks due inefficient curing times for large areas exposed to the laser beam..
Which is a Fdm Type of 3D Printer?
Fused deposition modeling (FDM) is a 3D printing technology that uses a continuous filament of thermoplastic material. The filament is fed through a heated extruder head, where it is melted and deposited in layers onto a build platform. FDM is the most common type of 3D printing technology and is used by many consumer and industrial 3D printers.
Why Is FDM Printing So Common?
Although 3D printers have only lately become well known, the technology has existed since the late 1980s. Large corporations have really been employing FDM printing for a while now, like Lego and BMW. As a result, it is well known and there is a ton of material accessible to assist with problem-solving.
One very significant factor that contributes to FDM’s success with the general population is that it is a far more economical kind of printing than, for instance, SLS or SLM, which employ lasers to produce items. These printers are readily cheap entry-level devices since they are easier to produce and less expensive to purchase. But there is a distinction in print quality.
The entrance hurdle for FDM printers is quite low. Although they appear to be simple to use and troubleshoot, more experienced users don’t feel constrained in any way because there are so many setting possibilities to experiment with. The size of the build area and the materials the printer can handle are actually the only true restrictions.
Conclusion
FDM 3D printing is a process of additive manufacturing that creates objects by depositing material in layers. It is the most common type of 3D printing and is used to create objects of all shapes and sizes. The material is melted and extruded through a nozzle in thin layers, which are then deposited on top of each other to build up the object.
This process can be used with a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even food.